Abstract
Secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) includes a heterogeneous group of diseases evolved from myelodysplasia, myeloproliferative disorders (MDS/ MPN), bone marrow failure syndrome or after exposure to leukemogenic agents such as chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy for malignant hematological (other malignant hematological diseases) or solid tumors.
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is the only potentially curative therapy but relapse is a frequent cause of failure after HCT occurring in more than 50% of patients. No systematic large analysis of HCT for sAML has evaluated risk factors and outcome based on a prior diagnosis of MDS or MPN. Therefore, the EBMT Acute Leukemia Working Party (ALWP) performed a multicenter retrospective registry study on patients undergoing HCT for sAML following MDS/MPN comparing myeloablative (MAC) to reduced intensity conditioning (RIC). ALWP-EBMT supplemental data forms were used to establish the occurrence of any prior hematological disorder or non-hematological malignancy as well as details of cytogenetic data and therapy.
We studied 811 patients with a previous diagnosis of MDS/ MPD and available cytogenetic data who had received HCT for sAML from an HLA-identical sibling (MRD, n=344 [42.4%]) or unrelated donor transplant (URD- 9/10 or 10/10) during 2000-16. Median time from diagnosis (sAML) to transplant was 137 days (IQR 94-204). Median age at HCT was 59.57 years (IQR 52-65). sAML with adverse cytogenetics accounted for 269 (33.2%) patients. At the time of HCT, 401 (49.5%) patients were in CR1 and 367 (45.3%) had active disease. Median follow-up of surviving patients was 32 months (IQR, 11-62).
Regimen intensity was assessed by EBMT criteria. MAC regimens were used in 326 (40.2%) patients while 485 (59.8%) received RIC. Older patients were more likely to receive RIC than MAC regimens (p<0.001). Most patients received peripheral blood stem cell grafts (n=731 [90.3%]; MAC 85.6% vs RIC 93.4%, p<0.001). A total of 534 (67.9%) patients were cytomegalovirus (CMV) seropositive pre-HCT. There were no significant differences in disease characteristics (e.g. disease status at transplant, cytogenetic risk category), donor source, year of transplant or CMV serology status between MAC and RIC cohorts. All patients received a calcineurin inhibitor-based combination as prophylaxis against graft versus host disease (GVHD) and 516 (63%) received in vivo T-cell depletion (rATG 474 (58%).
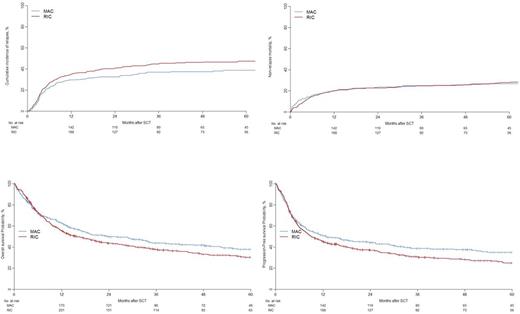
A total of 667 (95.2%) patients engrafted (MAC 94.5% vs. RIC 95.6%; p=0.596). Acute GVHD (grade II-IV) within 100 days of HCT occurred in 24% (95% CI, 21-27; MAC vs. RIC, p=0.126) and 2-year cumulative incidence of chronic GVHD was 33% (95% CI 30-37; MAC vs. RIC, p=0.150). Three-year cumulative incidence of relapse (RI) and non-relapse mortality (NRM) were 41% (95% CI, 38-45; MAC 37% [31-42] vs. RIC 45% [40-49], p=0.029) and 25% (95% CI, 22-28%, MAC 25% [20-30] vs. RIC 25% [21-29], p=0.959), respectively. The Kaplan-Meier estimate of overall survival (OS) and leukemia free survival (LFS) at 3 years were 40% (95% CI, 37-44; MAC 44% [38-50] vs. RIC 38% [33-43], p=0.041) and 34% (95% CI, 31-38; MAC 38% [33-45] vs. RIC 31% [27-36], p=0.032), respectively (Figure 1).
In multivariate analysis by Cox Regression, a higher RI was seen after RIC regimens (HR 1.72 [1.16-2.55]; p=0.0063). Patients receiving RIC regimens had a higher risk of chronic GVHD (HR 1.37 [1.02-1.84], p=0.0389). Non-relapse mortality (NRM) was equivalent in MAC and RIC groups.MAC regimens were associated with superior OS (HR 1.46, 95% CI 1.1-1.94; p=0.0085) and LFS (HR 1.37, 95% CI 1.02-1.85; p=0.0387). High risk cytogenetics and older age contributed significantly to inferior outcomes.
In summary, this EBMT registry study of HCT for sAML after MDS/MPN is the largest cohort reported. Myeloablative conditioning regimens were associated with a lower relapse risk and superior survival. Given that NRM after HCT has declined in the current era, these data indicate that the outcome of HCT for sAML may be improved by careful patient selection for MAC regimens. Survival may be further enhanced by effective pre-HCT disease control (also associated with decreased NRM) and post-HCT pre-emptive therapy to decrease RI.
Savani: Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Speakers Bureau. Ciceri: GSK: Other: B-thalassemia gene therapy was developed by Fondazione Telethon and Ospedale San Raffaele and has been inlicenced by GSK that provides funding for the clinical trial, Research Funding. Schmid: Celgene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MoilMed: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mohty: Sanofi: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal